New to Linux? Learn the basic Linux commands with this cheat sheet
Linux is the flavor for programmers and wannabe hackers today as it is slowly and steadily being adopted for standalone PCs in addition to networked PCs. One of the basic reasons it is so popular among coders and hackers is its rugged command line structure, unlike Windows and Mac based PCs.
Linux was designed around a strong and highly integrated command line interface. Windows and Mac don’t have that. This grants hackers and coder far greater access and control over their system and awesome customization. This is the reason that most hacking and pen testing tools are built into Linux have greater functionality above and beyond their windows counterparts. In contrast, Windows was built around the graphic user interface (GUI). This restrict user interaction to point-and-click navigation (slower) and application/system menu options for configuration.
One of the chief requirements to master Linux is to master its command line structure. Master the command line and you’ll be able to perform powerful tasks with just a few keystrokes.
The below cheat sheet will help you remember helpful Linux commands, whether you’re new to Linux or could just use a refresher.
Want To Learn Python? Click Here
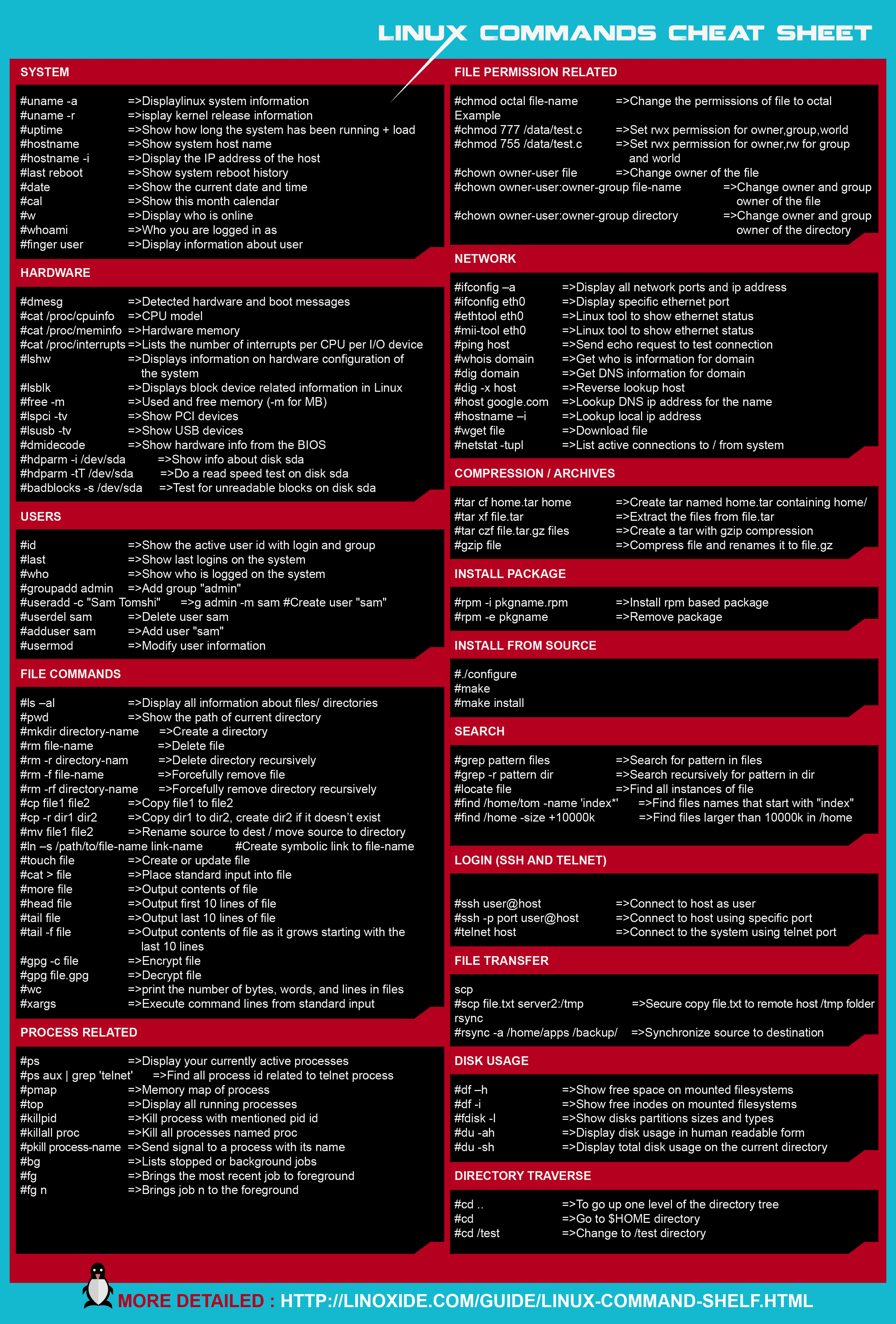
For those who wish to copy the commands in the image directly, here goes
- mkdir – make directories
Usage: mkdir [OPTION] DIRECTORY…
eg. mkdir lhn - ls – list directory contents
Usage: ls [OPTION]… [FILE]…
eg. ls, ls l, ls lhn - cd – changes directories
Usage: cd [DIRECTORY]
eg. cd lhn - pwd - print name of current working directory
Usage: pwd - vim – Vi Improved, a programmers text editor
Usage: vim [OPTION] [file]…
eg. vim lhn.txt - cp – copy files and directories
Usage: cp [OPTION]… SOURCE DEST
eg. cp sample.txt sample_copy.txt
cp sample_copy.txt target_dir - mv – move (rename) files
Usage: mv [OPTION]… SOURCE DEST
eg. mv source.txt target_dir
mv old.txt new.txt - rm remove files or directories
Usage: rm [OPTION]… FILE…
eg. rm file1.txt , rm rf some_dir - find – search for files in a directory hierarchy
Usage: find [OPTION] [path] [pattern] eg. find file1.txt, find name file1.txt - history – prints recently used commands
Usage: history - cat – concatenate files and print on the standard output
Usage: cat [OPTION] [FILE]…
eg. cat file1.txt file2.txt
cat n file1.txt - echo – display a line of text
Usage: echo [OPTION] [string] …
eg. echo I love India
echo $HOME - grep - print lines matching a pattern
Usage: grep [OPTION] PATTERN [FILE]…
eg. grep i apple sample.txt - wc - print the number of newlines, words, and bytes in files
Usage: wc [OPTION]… [FILE]…
eg. wc file1.txt
wc L file1.txt - sort – sort lines of text files
Usage: sort [OPTION]… [FILE]…
eg. sort file1.txt
sort r file1.txt - tar – to archive a file
Usage: tar [OPTION] DEST SOURCE
eg. tar cvf /home/archive.tar /home/original
tar xvf /home/archive.tar - kill – to kill a process(using signal mechanism)
Usage: kill [OPTION] pid
eg. kill 9 2275 - ps – report a snapshot of the current processes
Usage: ps [OPTION]
eg. ps, ps el - who – show who is logged on
Usage: who [OPTION]
eg. who , who b , who q - passwd – update a user’s authentication tokens(s)
Usage: passwd [OPTION]
eg. passwd - su – change user ID or become superuser
Usage: su [OPTION] [LOGIN]
eg. su remo, su - chown – change file owner and group
Usage: chown [OPTION]… OWNER[:[GROUP]] FILE…
eg. chown remo myfile.txt - chmod – change file access permissions
Usage: chmod [OPTION] [MODE] [FILE]
eg. chmod 744 calculate.sh - zip – package and compress (archive) files
Usage: zip [OPTION] DEST SOURSE
eg. zip original.zip original - unzip – list, test and extract compressed files in a ZIP archive
Usage: unzip filename
eg. unzip original.zi - ssh – SSH client (remote login program)
“ssh is a program for logging into a remote machine and for
executing commands on a remote machine”
Usage: ssh [options] [user]@hostname
eg. ssh X guest@10.105.11.20 - scp – secure copy (remote file copy program)
“scp copies files between hosts on a network”
Usage: scp [options] [[user]@host1:file1] [[user]@host2:file2]
eg. scp file1.txt guest@10.105.11.20:~/Desktop/ - fdisk – partition manipulator
eg. sudo fdisk l - mount – mount a file system
Usage: mount t type device dir
eg. mount /dev/sda5 /media/target - umount – unmount file systems
Usage: umount [OPTIONS] dir | device…
eg. umount /media/target - du – estimate file space usage
Usage: du [OPTION]… [FILE]…
eg. du - df – report filesystem disk space usage
Usage: df [OPTION]… [FILE]…
eg. df - quota – display disk usage and limits
Usage: quota [OPTION]
eg. quota v - reboot – reboot the system
Usage: reboot [OPTION]
eg. reboot - poweroff – power off the system
Usage: poweroff [OPTION]
eg. poweroff - kate – KDE Advanced Text Editor
Usage: kate [options][file(s)]
eg. kate file1.txt file2.txt - vim – Vi Improved, a programmers text editor
Usage: vim [OPTION] [file]…
eg. vi hello.c - gedit A text Editor. Used to create and edit files.
Usage: gedit [OPTION] [FILE]…
eg. gedit - bg – make a foreground process to run in background
Usage: type ‘ctrl+z’ and then ‘bg ‘ - fg – to make background process as foreground process
Usage: fg [jobid] - jobs – displays the names and ids of background jobs
Usage: jobs - sed stream editor for filtering and transforming text
Usage: sed [OPTION] [inputfile]…
eg. sed ‘s/love/hate/g’ loveletter.txt - awk pattern scanning and processing language
eg. awk F: ‘{ print $1 }’ sample_awk.txt - find search for files in a directory hierarchy
Usage: find [OPTION] [path] [pattern] eg. find name file1.txt - locate – find or locate a file
Usage: locate [OPTION]… FILE…
eg. locate file1.txt
The post Download This Cheat Sheet To Learn Basic Linux Commands appeared first on TechWorm.